diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..04775b42e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3110_score_of_a_string;
+
+// #Easy #String #2024_04_27_Time_1_ms_(99.93%)_Space_41.4_MB_(99.03%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int scoreOfString(String s) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) {
+ sum += Math.abs((s.charAt(i) - '0') - (s.charAt(i + 1) - '0'));
+ }
+ return sum;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1ad4aa7bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+3110\. Score of a String
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s`. The **score** of a string is defined as the sum of the absolute difference between the **ASCII** values of adjacent characters.
+
+Return the **score** of `s`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "hello"
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The **ASCII** values of the characters in `s` are: `'h' = 104`, `'e' = 101`, `'l' = 108`, `'o' = 111`. So, the score of `s` would be `|104 - 101| + |101 - 108| + |108 - 108| + |108 - 111| = 3 + 7 + 0 + 3 = 13`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "zaz"
+
+**Output:** 50
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The **ASCII** values of the characters in `s` are: `'z' = 122`, `'a' = 97`. So, the score of `s` would be `|122 - 97| + |97 - 122| = 25 + 25 = 50`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1b032f15a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Sorting #Greedy #2024_04_27_Time_4_ms_(99.55%)_Space_97.4_MB_(47.05%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int minRectanglesToCoverPoints(int[][] points, int w) {
+ Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
+ int res = 0;
+ int last = -1;
+ for (int[] a : points) {
+ if (a[0] > last) {
+ res++;
+ last = a[0] + w;
+ }
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3c48afd3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+3111\. Minimum Rectangles to Cover Points
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a 2D integer array `points`, where points[i] = [xi, yi]. You are also given an integer `w`. Your task is to **cover** **all** the given points with rectangles.
+
+Each rectangle has its lower end at some point (x1, 0) and its upper end at some point (x2, y2), where x1 <= x2, y2 >= 0, and the condition x2 - x1 <= w **must** be satisfied for each rectangle.
+
+A point is considered covered by a rectangle if it lies within or on the boundary of the rectangle.
+
+Return an integer denoting the **minimum** number of rectangles needed so that each point is covered by **at least one** rectangle_._
+
+**Note:** A point may be covered by more than one rectangle.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
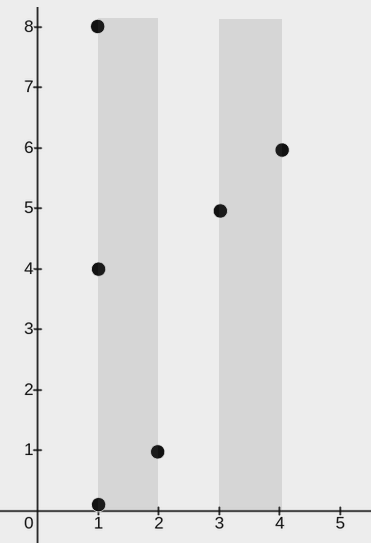
+
+
+**Input:** points = [[2,1],[1,0],[1,4],[1,8],[3,5],[4,6]], w = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The image above shows one possible placement of rectangles to cover the points:
+
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(1, 0)` and its upper end at `(2, 8)`
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(3, 0)` and its upper end at `(4, 8)`
+
+**Example 2:**
+
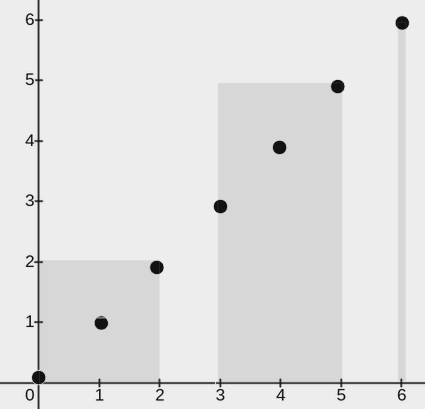
+
+
+**Input:** points = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[4,4],[5,5],[6,6]], w = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The image above shows one possible placement of rectangles to cover the points:
+
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(0, 0)` and its upper end at `(2, 2)`
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(3, 0)` and its upper end at `(5, 5)`
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(6, 0)` and its upper end at `(6, 6)`
+
+**Example 3:**
+
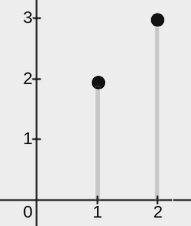
+
+
+**Input:** points = [[2,3],[1,2]], w = 0
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The image above shows one possible placement of rectangles to cover the points:
+
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(1, 0)` and its upper end at `(1, 2)`
+* A rectangle with a lower end at `(2, 0)` and its upper end at `(2, 3)`
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= points.length <= 105
+* `points[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= xi == points[i][0] <= 109
+* 0 <= yi == points[i][1] <= 109
+* 0 <= w <= 109
+* All pairs (xi, yi) are distinct.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2d4048e8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Heap_Priority_Queue #Graph #Shortest_Path
+// #2024_04_27_Time_10_ms_(100.00%)_Space_85.4_MB_(99.80%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] minimumTime(int n, int[][] edges, int[] disappear) {
+ int[] dist = new int[n];
+ Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
+ boolean exit = false;
+ int i;
+ int src;
+ int dest;
+ int cost;
+ dist[0] = 0;
+ for (i = 0; i < n && !exit; ++i) {
+ exit = true;
+ for (int[] edge : edges) {
+ src = edge[0];
+ dest = edge[1];
+ cost = edge[2];
+ if (dist[src] != -1
+ && dist[src] != Integer.MAX_VALUE
+ && dist[src] < disappear[src]
+ && dist[src] + cost < dist[dest]) {
+ exit = false;
+ dist[dest] = dist[src] + cost;
+ }
+ if (dist[dest] != -1
+ && dist[dest] != Integer.MAX_VALUE
+ && dist[dest] < disappear[dest]
+ && dist[dest] + cost < dist[src]) {
+ exit = false;
+ dist[src] = dist[dest] + cost;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ for (i = 0; i < dist.length; ++i) {
+ if (dist[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE || dist[i] >= disappear[i]) {
+ dist[i] = -1;
+ }
+ }
+ return dist;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7f330dc2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+3112\. Minimum Time to Visit Disappearing Nodes
+
+Medium
+
+There is an undirected graph of `n` nodes. You are given a 2D array `edges`, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, lengthi] describes an edge between node ui and node vi with a traversal time of lengthi units.
+
+Additionally, you are given an array `disappear`, where `disappear[i]` denotes the time when the node `i` disappears from the graph and you won't be able to visit it.
+
+**Notice** that the graph might be disconnected and might contain multiple edges.
+
+Return the array `answer`, with `answer[i]` denoting the **minimum** units of time required to reach node `i` from node 0. If node `i` is **unreachable** from node 0 then `answer[i]` is `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
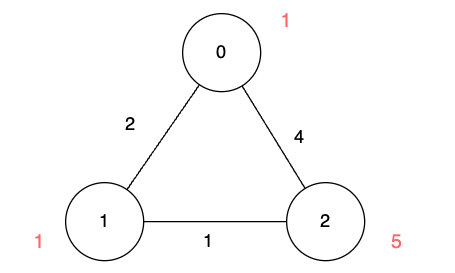
+
+
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[1,2,1],[0,2,4]], disappear = [1,1,5]
+
+**Output:** [0,-1,4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We are starting our journey from node 0, and our goal is to find the minimum time required to reach each node before it disappears.
+
+* For node 0, we don't need any time as it is our starting point.
+* For node 1, we need at least 2 units of time to traverse `edges[0]`. Unfortunately, it disappears at that moment, so we won't be able to visit it.
+* For node 2, we need at least 4 units of time to traverse `edges[2]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
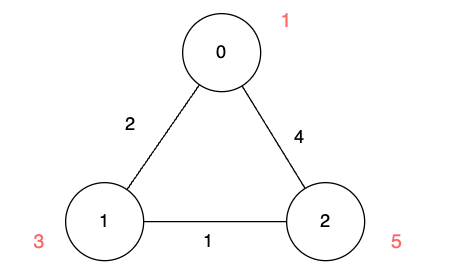
+
+
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[1,2,1],[0,2,4]], disappear = [1,3,5]
+
+**Output:** [0,2,3]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We are starting our journey from node 0, and our goal is to find the minimum time required to reach each node before it disappears.
+
+* For node 0, we don't need any time as it is the starting point.
+* For node 1, we need at least 2 units of time to traverse `edges[0]`.
+* For node 2, we need at least 3 units of time to traverse `edges[0]` and `edges[1]`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, edges = [[0,1,1]], disappear = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** [0,-1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Exactly when we reach node 1, it disappears.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* 0 <= edges.length <= 105
+* edges[i] == [ui, vi, lengthi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1
+* 1 <= lengthi <= 105
+* `disappear.length == n`
+* 1 <= disappear[i] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b69f93cfe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Binary_Search #Stack #Monotonic_Stack
+// #2024_04_27_Time_13_ms_(98.83%)_Space_60.4_MB_(67.66%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayDeque;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public long numberOfSubarrays(int[] nums) {
+ ArrayDeque stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ long res = 0;
+ for (int a : nums) {
+ while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()[0] < a) {
+ stack.pop();
+ }
+ if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek()[0] != a) {
+ stack.push(new int[] {a, 0});
+ }
+ res += ++stack.peek()[1];
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7cff5a6ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+3113\. Find the Number of Subarrays Where Boundary Elements Are Maximum
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array of **positive** integers `nums`.
+
+Return the number of subarrays of `nums`, where the **first** and the **last** elements of the subarray are _equal_ to the **largest** element in the subarray.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,4,3,3,2]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 6 subarrays which have the first and the last elements equal to the largest element of the subarray:
+
+* subarray [**1**,4,3,3,2], with its largest element 1. The first element is 1 and the last element is also 1.
+* subarray [1,**4**,3,3,2], with its largest element 4. The first element is 4 and the last element is also 4.
+* subarray [1,4,**3**,3,2], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [1,4,3,**3**,2], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [1,4,3,3,**2**], with its largest element 2. The first element is 2 and the last element is also 2.
+* subarray [1,4,**3,3**,2], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+
+Hence, we return 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,3,3]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 6 subarrays which have the first and the last elements equal to the largest element of the subarray:
+
+* subarray [**3**,3,3], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [3,**3**,3], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [3,3,**3**], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [**3,3**,3], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [3,**3,3**], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+* subarray [**3,3,3**], with its largest element 3. The first element is 3 and the last element is also 3.
+
+Hence, we return 6.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There is a single subarray of `nums` which is [**1**], with its largest element 1. The first element is 1 and the last element is also 1.
+
+Hence, we return 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7ce927d28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters;
+
+// #Easy #String #Enumeration #2024_04_27_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_42.5_MB_(85.42%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public String findLatestTime(String s) {
+ StringBuilder nm = new StringBuilder();
+ if (s.charAt(0) == '?' && s.charAt(1) == '?') {
+ nm.append("11");
+ } else if (s.charAt(0) != '?' && s.charAt(1) == '?') {
+ nm.append(s.charAt(0));
+ if (s.charAt(0) == '1') {
+ nm.append("1");
+ } else {
+ nm.append("9");
+ }
+ } else if (s.charAt(0) == '?' && s.charAt(1) != '?') {
+ if (s.charAt(1) >= '2' && s.charAt(1) <= '9') {
+ nm.append("0");
+ } else {
+ nm.append("1");
+ }
+ nm.append(s.charAt(1));
+ } else {
+ nm.append(s.charAt(0));
+ nm.append(s.charAt(1));
+ }
+ nm.append(":");
+ if (s.charAt(3) == '?' && s.charAt(4) == '?') {
+ nm.append("59");
+ } else if (s.charAt(3) != '?' && s.charAt(4) == '?') {
+ nm.append(s.charAt(3));
+ nm.append("9");
+ } else if (s.charAt(3) == '?' && s.charAt(4) != '?') {
+ nm.append("5");
+ nm.append(s.charAt(4));
+ } else {
+ nm.append(s.charAt(3));
+ nm.append(s.charAt(4));
+ }
+ return nm.toString();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fb955d8c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+3114\. Latest Time You Can Obtain After Replacing Characters
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` representing a 12-hour format time where some of the digits (possibly none) are replaced with a `"?"`.
+
+12-hour times are formatted as `"HH:MM"`, where `HH` is between `00` and `11`, and `MM` is between `00` and `59`. The earliest 12-hour time is `00:00`, and the latest is `11:59`.
+
+You have to replace **all** the `"?"` characters in `s` with digits such that the time we obtain by the resulting string is a **valid** 12-hour format time and is the **latest** possible.
+
+Return _the resulting string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "1?:?4"
+
+**Output:** "11:54"
+
+**Explanation:** The latest 12-hour format time we can achieve by replacing `"?"` characters is `"11:54"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "0?:5?"
+
+**Output:** "09:59"
+
+**Explanation:** The latest 12-hour format time we can achieve by replacing `"?"` characters is `"09:59"`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `s.length == 5`
+* `s[2]` is equal to the character `":"`.
+* All characters except `s[2]` are digits or `"?"` characters.
+* The input is generated such that there is **at least** one time between `"00:00"` and `"11:59"` that you can obtain after replacing the `"?"` characters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1623e6361
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3115_maximum_prime_difference;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Math #Number_Theory #2024_04_27_Time_1_ms_(99.91%)_Space_79.5_MB_(32.00%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int maximumPrimeDifference(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int i = 0;
+ while (i < n && check(nums[i])) {
+ i++;
+ }
+ int j = n - 1;
+ while (j >= 0 && check(nums[j])) {
+ j--;
+ }
+ return j - i;
+ }
+
+ private boolean check(int n) {
+ if (n < 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
+ if (n % i == 0) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6ddebcacd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+3115\. Maximum Prime Difference
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`.
+
+Return an integer that is the **maximum** distance between the **indices** of two (not necessarily different) prime numbers in `nums`_._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,2,9,5,3]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** `nums[1]`, `nums[3]`, and `nums[4]` are prime. So the answer is `|4 - 1| = 3`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,8,2,8]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** `nums[2]` is prime. Because there is just one prime number, the answer is `|2 - 2| = 0`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 105
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 100`
+* The input is generated such that the number of prime numbers in the `nums` is at least one.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..36aa08920
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Math #Binary_Search #Bit_Manipulation #Number_Theory #Combinatorics
+// #2024_04_27_Time_2_ms_(100.00%)_Space_41.4_MB_(72.21%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+@SuppressWarnings("java:S1119")
+public class Solution {
+ public long findKthSmallest(int[] coins, int k) {
+ int minC = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ for (int c : coins) {
+ minC = Math.min(minC, c);
+ }
+ long[] cc = coins(coins);
+ long max = (long) minC * k;
+ long min = max / coins.length;
+ while (min < max) {
+ long mid = (min + max) / 2;
+ final long cnt = count(cc, mid);
+ if (cnt > k) {
+ max = mid - 1;
+ } else if (cnt < k) {
+ min = mid + 1;
+ } else {
+ max = mid;
+ }
+ }
+ return min;
+ }
+
+ private long count(long[] coins, long v) {
+ long r = 0;
+ for (long c : coins) {
+ r += v / c;
+ }
+ return r;
+ }
+
+ private long[] coins(int[] coins) {
+ Arrays.sort(coins);
+ int len = 1;
+ a:
+ for (int i = 1; i < coins.length; i++) {
+ final int c = coins[i];
+ for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
+ if (c % coins[j] == 0) {
+ continue a;
+ }
+ }
+ coins[len++] = c;
+ }
+ coins = Arrays.copyOf(coins, len);
+ long[] res = new long[(1 << coins.length) - 1];
+ iterate(coins, res, 1, 0, 0, true);
+ return res;
+ }
+
+ private int iterate(int[] coins, long[] res, long mult, int start, int idx, boolean positive) {
+ for (int i = start; i < coins.length; i++) {
+ long next = mult * coins[i] / gcd(mult, coins[i]);
+ res[idx++] = positive ? next : -next;
+ idx = iterate(coins, res, next, i + 1, idx, !positive);
+ }
+ return idx;
+ }
+
+ private long gcd(long a, long b) {
+ return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8d70f8493
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+3116\. Kth Smallest Amount With Single Denomination Combination
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer array `coins` representing coins of different denominations and an integer `k`.
+
+You have an infinite number of coins of each denomination. However, you are **not allowed** to combine coins of different denominations.
+
+Return the kth **smallest** amount that can be made using these coins.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** coins = [3,6,9], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** The given coins can make the following amounts:
+
+ Coin 3 produces multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, etc.
+
+ Coin 6 produces multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, etc.
+
+ Coin 9 produces multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, etc.
+
+ All of the coins combined produce: 3, 6, **9**, 12, 15, etc.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** coins = [5,2], k = 7
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:** The given coins can make the following amounts:
+
+ Coin 5 produces multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, etc.
+
+ Coin 2 produces multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, etc.
+
+ All of the coins combined produce: 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, **12**, 14, 15, etc.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= coins.length <= 15`
+* `1 <= coins[i] <= 25`
+* 1 <= k <= 2 * 109
+* `coins` contains pairwise distinct integers.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..56b9df045
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Binary_Search #Bit_Manipulation #Queue #Segment_Tree
+// #2024_04_27_Time_6_ms_(100.00%)_Space_44.8_MB_(99.04%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private static final int INF = 0xfffffff;
+
+ public int minimumValueSum(int[] nums, int[] andValues) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
+ Arrays.fill(dp, INF);
+ dp[0] = 0;
+ for (int target : andValues) {
+ int sum = INF;
+ int minSum = INF;
+ int rightSum = INF;
+ int[] leftSum = new int[n + 1];
+ leftSum[0] = INF;
+ int left = 0;
+ int right = 0;
+ int[] nextdp = new int[n + 1];
+ nextdp[0] = INF;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ sum &= nums[i];
+ rightSum &= nums[i];
+ ++right;
+ if (sum < target) {
+ minSum = INF;
+ sum = nums[i];
+ }
+ while ((leftSum[left] & rightSum) <= target) {
+ if ((leftSum[left] & rightSum) == target) {
+ minSum = Math.min(minSum, dp[i - left - right + 1]);
+ }
+ if (left-- > 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ left = right;
+ int start = i;
+ for (int l = 1; l <= left; ++l) {
+ leftSum[l] = leftSum[l - 1] & nums[start--];
+ }
+ right = 0;
+ rightSum = INF;
+ }
+ nextdp[i + 1] = minSum + nums[i];
+ }
+ dp = nextdp;
+ }
+ return dp[n] < INF ? dp[n] : -1;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0b0b0bec8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+3117\. Minimum Sum of Values by Dividing Array
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two arrays `nums` and `andValues` of length `n` and `m` respectively.
+
+The **value** of an array is equal to the **last** element of that array.
+
+You have to divide `nums` into `m` **disjoint contiguous** subarrays such that for the ith subarray [li, ri], the bitwise `AND` of the subarray elements is equal to `andValues[i]`, in other words, nums[li] & nums[li + 1] & ... & nums[ri] == andValues[i] for all `1 <= i <= m`, where `&` represents the bitwise `AND` operator.
+
+Return _the **minimum** possible sum of the **values** of the_ `m` _subarrays_ `nums` _is divided into_. _If it is not possible to divide_ `nums` _into_ `m` _subarrays satisfying these conditions, return_ `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,4,3,3,2], andValues = [0,3,3,2]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only possible way to divide `nums` is:
+
+1. `[1,4]` as `1 & 4 == 0`.
+2. `[3]` as the bitwise `AND` of a single element subarray is that element itself.
+3. `[3]` as the bitwise `AND` of a single element subarray is that element itself.
+4. `[2]` as the bitwise `AND` of a single element subarray is that element itself.
+
+The sum of the values for these subarrays is `4 + 3 + 3 + 2 = 12`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,5,7,7,7,5], andValues = [0,7,5]
+
+**Output:** 17
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are three ways to divide `nums`:
+
+1. `[[2,3,5],[7,7,7],[5]]` with the sum of the values `5 + 7 + 5 == 17`.
+2. `[[2,3,5,7],[7,7],[5]]` with the sum of the values `7 + 7 + 5 == 19`.
+3. `[[2,3,5,7,7],[7],[5]]` with the sum of the values `7 + 7 + 5 == 19`.
+
+The minimum possible sum of the values is `17`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4], andValues = [2]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The bitwise `AND` of the entire array `nums` is `0`. As there is no possible way to divide `nums` into a single subarray to have the bitwise `AND` of elements `2`, return `-1`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n == nums.length <= 104
+* `1 <= m == andValues.length <= min(n, 10)`
+* 1 <= nums[i] < 105
+* 0 <= andValues[j] < 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3514174b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i;
+
+// #Easy #String #Hash_Table #2024_04_27_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_41.9_MB_(92.08%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int numberOfSpecialChars(String word) {
+ int[] a = new int[26];
+ int[] b = new int[26];
+ int ans = 0;
+ for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
+ if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {
+ a[c - 'a']++;
+ } else {
+ b[c - 'A']++;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
+ if (a[i] != 0 && b[i] != 0) {
+ ans++;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..66a0e8b7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+3120\. Count the Number of Special Characters I
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `word`. A letter is called **special** if it appears **both** in lowercase and uppercase in `word`.
+
+Return the number of **special** letters in `word`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** word = "aaAbcBC"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The special characters in `word` are `'a'`, `'b'`, and `'c'`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** word = "abc"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No character in `word` appears in uppercase.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** word = "abBCab"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only special character in `word` is `'b'`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= word.length <= 50`
+* `word` consists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5104c264b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii;
+
+// #Medium #String #Hash_Table #2024_04_27_Time_6_ms_(100.00%)_Space_45.2_MB_(97.93%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int numberOfSpecialChars(String word) {
+ int[] small = new int[26];
+ Arrays.fill(small, -1);
+ int[] capital = new int[26];
+ Arrays.fill(capital, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
+ char a = word.charAt(i);
+ if (a < 91) {
+ capital[a - 65] = Math.min(capital[a - 65], i);
+ } else {
+ small[a - 97] = i;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
+ if (-1 != small[i] && Integer.MAX_VALUE != capital[i] && capital[i] > small[i]) {
+ result++;
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4b2ddaba9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+3121\. Count the Number of Special Characters II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `word`. A letter `c` is called **special** if it appears **both** in lowercase and uppercase in `word`, and **every** lowercase occurrence of `c` appears before the **first** uppercase occurrence of `c`.
+
+Return the number of **special** letters in `word`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** word = "aaAbcBC"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The special characters are `'a'`, `'b'`, and `'c'`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** word = "abc"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are no special characters in `word`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** word = "AbBCab"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are no special characters in `word`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= word.length <= 2 * 105
+* `word` consists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..08adf8ca1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Matrix
+// #2024_04_27_Time_6_ms_(100.00%)_Space_156.6_MB_(54.30%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int minimumOperations(int[][] grid) {
+ int n = grid.length;
+ int m = grid[0].length;
+ int[][] dp = new int[m][10];
+ int[][] cnt = new int[m][10];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
+ cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++;
+ }
+ }
+ int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ int second = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ int firstId = -1;
+ int secondId = -1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
+ dp[0][i] = n - cnt[0][i];
+ if (dp[0][i] <= first) {
+ second = first;
+ first = dp[0][i];
+ secondId = firstId;
+ firstId = i;
+ } else if (dp[0][i] < second) {
+ second = dp[0][i];
+ secondId = i;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int j = 1; j < m; ++j) {
+ int lastFirstId = firstId;
+ int lastSecondId = secondId;
+ first = second = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ firstId = secondId = -1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
+ int tmp;
+ int fix = n - cnt[j][i];
+ if (i == lastFirstId) {
+ tmp = fix + dp[j - 1][lastSecondId];
+ } else {
+ tmp = fix + dp[j - 1][lastFirstId];
+ }
+ if (tmp <= first) {
+ second = first;
+ first = tmp;
+ secondId = firstId;
+ firstId = i;
+ } else if (tmp < second) {
+ second = tmp;
+ secondId = i;
+ }
+ dp[j][i] = tmp;
+ }
+ }
+ int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, dp[m - 1][i]);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1bc037bce
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+3122\. Minimum Number of Operations to Satisfy Conditions
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a 2D matrix `grid` of size `m x n`. In one **operation**, you can change the value of **any** cell to **any** non-negative number. You need to perform some **operations** such that each cell `grid[i][j]` is:
+
+* Equal to the cell below it, i.e. `grid[i][j] == grid[i + 1][j]` (if it exists).
+* Different from the cell to its right, i.e. `grid[i][j] != grid[i][j + 1]` (if it exists).
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations needed.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0,2],[1,0,2]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**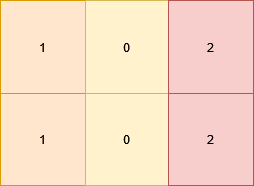**
+
+All the cells in the matrix already satisfy the properties.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**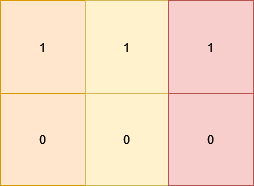**
+
+The matrix becomes `[[1,0,1],[1,0,1]]` which satisfies the properties, by doing these 3 operations:
+
+* Change `grid[1][0]` to 1.
+* Change `grid[0][1]` to 0.
+* Change `grid[1][2]` to 1.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1],[2],[3]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+There is a single column. We can change the value to 1 in each cell using 2 operations.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n, m <= 1000`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 9`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ef79e0076
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths;
+
+// #Hard #Heap_Priority_Queue #Graph #Shortest_Path #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search
+// #2024_04_27_Time_24_ms_(100.00%)_Space_75.2_MB_(88.50%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import java.util.PriorityQueue;
+
+@SuppressWarnings({"java:S135", "java:S2234"})
+public class Solution {
+ private int[] edge;
+ private int[] weight;
+ private int[] next;
+ private int[] head;
+ private int index;
+
+ private void add(int u, int v, int w) {
+ edge[index] = v;
+ weight[index] = w;
+ next[index] = head[u];
+ head[u] = index++;
+ }
+
+ public boolean[] findAnswer(int n, int[][] edges) {
+ int m = edges.length;
+ edge = new int[m << 1];
+ weight = new int[m << 1];
+ next = new int[m << 1];
+ head = new int[n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ head[i] = -1;
+ }
+ index = 0;
+ for (int[] localEdge : edges) {
+ int u = localEdge[0];
+ int v = localEdge[1];
+ int w = localEdge[2];
+ add(u, v, w);
+ add(v, u, w);
+ }
+ PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[1] < b[1] ? -1 : 1);
+ long[] distances = new long[n];
+ Arrays.fill(distances, (long) 1e12);
+ pq.offer(new long[] {0, 0});
+ distances[0] = 0;
+ while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
+ long[] cur = pq.poll();
+ int u = (int) cur[0];
+ long distance = cur[1];
+ if (distance > distances[u]) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (u == n - 1) {
+ break;
+ }
+ for (int localIndex = head[u]; localIndex != -1; localIndex = next[localIndex]) {
+ int v = edge[localIndex];
+ int w = weight[localIndex];
+ long newDistance = distance + w;
+ if (newDistance < distances[v]) {
+ distances[v] = newDistance;
+ pq.offer(new long[] {v, newDistance});
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ boolean[] ans = new boolean[m];
+ if (distances[n - 1] >= (long) 1e12) {
+ return ans;
+ }
+ dfs(distances, n - 1, -1, ans);
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(long[] distances, int u, int pre, boolean[] ans) {
+ for (int localIndex = head[u]; localIndex != -1; localIndex = next[localIndex]) {
+ int v = edge[localIndex];
+ int w = weight[localIndex];
+ int i = localIndex >> 1;
+ if (distances[v] + w != distances[u]) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ ans[i] = true;
+ if (v == pre) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ dfs(distances, v, u, ans);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..012584c1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+3123\. Find Edges in Shortest Paths
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an undirected weighted graph of `n` nodes numbered from 0 to `n - 1`. The graph consists of `m` edges represented by a 2D array `edges`, where edges[i] = [ai, bi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi with weight wi.
+
+Consider all the shortest paths from node 0 to node `n - 1` in the graph. You need to find a **boolean** array `answer` where `answer[i]` is `true` if the edge `edges[i]` is part of **at least** one shortest path. Otherwise, `answer[i]` is `false`.
+
+Return the array `answer`.
+
+**Note** that the graph may not be connected.
+
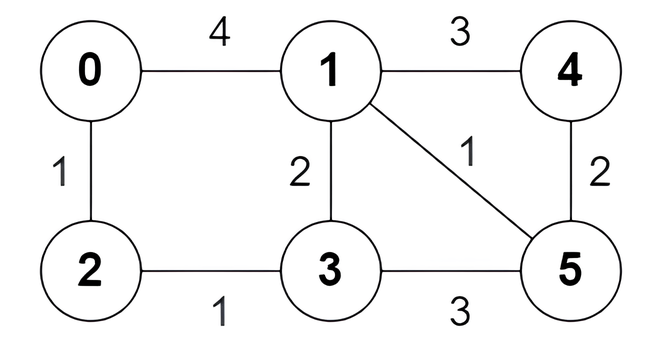
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 6, edges = [[0,1,4],[0,2,1],[1,3,2],[1,4,3],[1,5,1],[2,3,1],[3,5,3],[4,5,2]]
+
+**Output:** [true,true,true,false,true,true,true,false]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The following are **all** the shortest paths between nodes 0 and 5:
+
+* The path `0 -> 1 -> 5`: The sum of weights is `4 + 1 = 5`.
+* The path `0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5`: The sum of weights is `1 + 1 + 3 = 5`.
+* The path `0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1 -> 5`: The sum of weights is `1 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 5`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
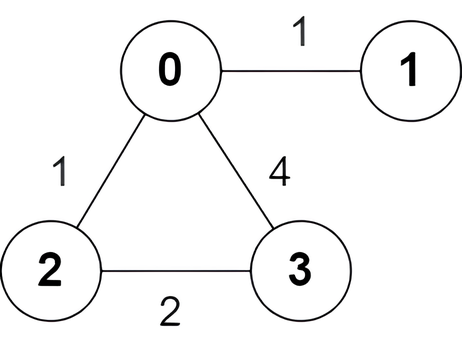
+
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = [[2,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,3,4],[3,2,2]]
+
+**Output:** [true,false,false,true]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There is one shortest path between nodes 0 and 3, which is the path `0 -> 2 -> 3` with the sum of weights `1 + 2 = 3`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `m == edges.length`
+* 1 <= m <= min(5 * 104, n * (n - 1) / 2)
+* 0 <= ai, bi < n
+* ai != bi
+* 1 <= wi <= 105
+* There are no repeated edges.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e51d8136e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3110_score_of_a_string/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3110_score_of_a_string;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void scoreOfString() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().scoreOfString("hello"), equalTo(13));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void scoreOfString2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().scoreOfString("zaz"), equalTo(50));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3e7af5c9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3111_minimum_rectangles_to_cover_points;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minRectanglesToCoverPoints() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .minRectanglesToCoverPoints(
+ new int[][] {{2, 1}, {1, 0}, {1, 4}, {1, 8}, {3, 5}, {4, 6}}, 1),
+ equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minRectanglesToCoverPoints2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .minRectanglesToCoverPoints(
+ new int[][] {
+ {0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {3, 3}, {4, 4}, {5, 5}, {6, 6}
+ },
+ 2),
+ equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minRectanglesToCoverPoints3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minRectanglesToCoverPoints(new int[][] {{2, 3}, {1, 2}}, 0),
+ equalTo(2));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9cefed87f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3112_minimum_time_to_visit_disappearing_nodes;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minimumTime() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .minimumTime(
+ 3,
+ new int[][] {{0, 1, 2}, {1, 2, 1}, {0, 2, 4}},
+ new int[] {1, 1, 5}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {0, -1, 4}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumTime2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .minimumTime(
+ 3,
+ new int[][] {{0, 1, 2}, {1, 2, 1}, {0, 2, 4}},
+ new int[] {1, 3, 5}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {0, 2, 3}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumTime3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minimumTime(2, new int[][] {{0, 1, 1}}, new int[] {1, 1}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {0, -1}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..dbeb59f66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3113_find_the_number_of_subarrays_where_boundary_elements_are_maximum;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSubarrays() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSubarrays(new int[] {1, 4, 3, 3, 2}), equalTo(6L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSubarrays2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSubarrays(new int[] {3, 3, 3}), equalTo(6L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSubarrays3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSubarrays(new int[] {1}), equalTo(1L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..bd0d01819
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3114_latest_time_you_can_obtain_after_replacing_characters;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("1?:?4"), equalTo("11:54"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("0?:5?"), equalTo("09:59"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("?1:?6"), equalTo("11:56"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime4() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("08:33"), equalTo("08:33"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime5() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("??:1?"), equalTo("11:19"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime6() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("04:??"), equalTo("04:59"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findLatestTime7() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findLatestTime("?3:12"), equalTo("03:12"));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e4abd0267
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3115_maximum_prime_difference/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3115_maximum_prime_difference;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void maximumPrimeDifference() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().maximumPrimeDifference(new int[] {4, 2, 9, 5, 3}), equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void maximumPrimeDifference2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().maximumPrimeDifference(new int[] {4, 8, 2, 8}), equalTo(0));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3cf0a0b7d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3116_kth_smallest_amount_with_single_denomination_combination;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void findKthSmallest() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findKthSmallest(new int[] {3, 6, 9}, 3), equalTo(9L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findKthSmallest2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().findKthSmallest(new int[] {5, 2}, 7), equalTo(12L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..efc7f3d58
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3117_minimum_sum_of_values_by_dividing_array;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minimumValueSum() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minimumValueSum(new int[] {1, 4, 3, 3, 2}, new int[] {0, 3, 3, 2}),
+ equalTo(12));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumValueSum2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .minimumValueSum(new int[] {2, 3, 5, 7, 7, 7, 5}, new int[] {0, 7, 5}),
+ equalTo(17));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumValueSum3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minimumValueSum(new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[] {2}), equalTo(-1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..835fc2716
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3120_count_the_number_of_special_characters_i;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("aaAbcBC"), equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("abc"), equalTo(0));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("abBCab"), equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a8608a43d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3121_count_the_number_of_special_characters_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("aaAbcBC"), equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("abc"), equalTo(0));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfSpecialChars3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfSpecialChars("AbBCab"), equalTo(0));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5970083e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3122_minimum_number_of_operations_to_satisfy_conditions;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minimumOperations() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minimumOperations(new int[][] {{1, 0, 2}, {1, 0, 2}}), equalTo(0));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumOperations2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minimumOperations(new int[][] {{1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 0}}), equalTo(3));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d378cece0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3101_3200/s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3123_find_edges_in_shortest_paths;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void findAnswer() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .findAnswer(
+ 6,
+ new int[][] {
+ {0, 1, 4}, {0, 2, 1}, {1, 3, 2}, {1, 4, 3}, {1, 5, 1},
+ {2, 3, 1}, {3, 5, 3}, {4, 5, 2}
+ }),
+ equalTo(new boolean[] {true, true, true, false, true, true, true, false}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findAnswer2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .findAnswer(4, new int[][] {{2, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1}, {0, 3, 4}, {3, 2, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new boolean[] {true, false, false, true}));
+ }
+}